Shipping Lead Time: How It Works and How To Reduce It
Shipping lead time is the time between when an order is placed and when it’s delivered. It includes the time spent processing the order, handling the goods, and delivering the package. Lead time is a crucial metric for businesses that rely on shipments to fulfill orders.
For example, a manufacturer might need between two weeks and eight months to deliver new cars after the buyer places an order. Because lead times affect every step of the fulfillment process, many merchants invest heavily in decreasing this timeframe.
For online merchants, lead time includes tasks such as storage, stock maintenance, order processing, and shipments.
In this blog post, we will explain what shipping lead time is, how it affects freight rates, why it is important to reduce it, and how DIDADI Logistics Tech can help you achieve that.
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes to complete a process or deliver a product or service from the initiation of an order or request to its fulfillment. It encompasses all the steps, procedures, and activities involved in fulfilling a request, including processing, production, transportation, and delivery.
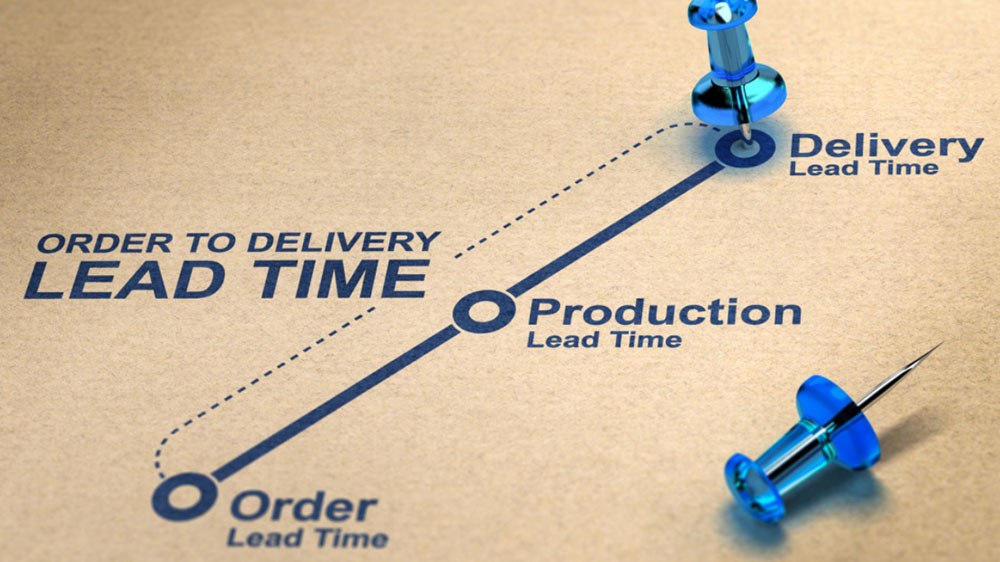
In shipping and logistics, lead time specifically pertains to the time it takes for goods to be delivered from the moment an order is placed to the moment it is received by the customer. There are several types of lead time in shipping:
Manufacturing Lead Time: The time it takes to produce a product after an order is placed.
Order Processing Lead Time: The time it takes to process an order, including order confirmation, picking, and packing.
Shipping Lead Time: The time it takes for products to be transported from the source to the destination.
Delivery Lead Time: The time it takes for the products to be delivered from the distribution center to the customer.
Several factors can influence lead time in shipping and various industries:
Production Processes: The complexity and efficiency of manufacturing or production processes.
Supplier Lead Time: The time it takes for suppliers to deliver raw materials or components.
Inventory Levels: The amount of stock on hand can affect how quickly an order can be fulfilled.
Transportation and Logistics: The availability and speed of transportation methods.
Order Volume: Larger orders may require more time to process and fulfill.
Customization: Custom or made-to-order products typically have longer lead times.
Lead time is calculated by measuring the time that elapses between the initiation of an order and its fulfillment. Here’s a basic formula:
Lead Time = End Time – Start Time
In shipping and logistics, you would use specific start and end times related to order placement and order receipt or delivery.
Cycle time and lead time are two important metrics used in various industries, especially in manufacturing, software development, and project management. They provide valuable insights into the efficiency and performance of processes. Here’s everything you should know about cycle time and lead time:
Cycle Time
Definition
Cycle time refers to the time it takes to complete a single unit of work or a task within a process. It measures the duration from the moment a work item is started until it is finished.
Focus
Cycle time is primarily focused on the internal efficiency of a process. It helps organizations understand how quickly they can produce or deliver a specific item once the work begins.
Usage
Commonly used in manufacturing, cycle time can be applied to various processes, including production lines, software development sprints, and customer service response times.
Monitoring and Improvement
Organizations use cycle time to identify bottlenecks, optimize workflows, and improve process efficiency. Reducing cycle time often leads to cost savings and improved customer satisfaction.
Example
In a software development context, cycle time could measure how long it takes to code and test a single feature or user story within a sprint.Definition
Lead time is the total time it takes for a work item to move through a process from the moment it is requested or initiated until it is delivered or completed. It encompasses both active work time and any waiting time in queues or backlogs.
Focus
Lead time provides a broader perspective than cycle time. It includes not only the time required to complete the work but also any delays or wait times that occur between process steps.
Usage
Lead time is commonly used in supply chain management, order fulfillment, and project planning to estimate delivery times and manage customer expectations.
Monitoring and Improvement
Organizations use lead time to identify potential delays, streamline processes, and set realistic expectations for customers. Reducing lead time can lead to faster delivery and improved customer satisfaction.Example
In Direct-to-consumer (DTC) retailer business, lead time would include the time from when a customer places an order to when the order is delivered, including order processing, packaging, and shipping.Key Differences
Scope
Cycle time measures the time it takes to complete a specific task or unit of work, while lead time measures the entire duration from initiation to completion, including any waiting or queue time.Focus
Cycle time focuses on internal process efficiency, while lead time considers the end-to-end customer experience and external factors like waiting and queuing.
Application
Cycle time is often used for process optimization within a specific department or team, while lead time is more holistic and is used to manage customer expectations and plan overall process flow.Freight rates are the fees charged by carriers for transporting goods from one place to another. They depend on various factors, such as:
Distance: The longer the distance, the higher the freight rate.
Weight and volume: The heavier and larger the cargo, the higher the freight rate.
Mode of transport: Air freight is faster but more expensive than sea freight.
Fuel price: The higher the fuel price, the higher the freight rate.
Seasonality: The demand and supply of cargo space fluctuate according to different seasons, holidays, and events. For example, peak season surcharges are applied during high-demand periods such as Christmas or Chinese New Year.
Exchange rate: The currency fluctuations affect the freight rate in different countries.
Short lead time means the time between receiving an order and delivering it to the customer is reduced as much as possible. This can have many benefits for both parties, such as:
Urgency and Expedited Shipping
When you have a shorter lead time and need to get your goods to their destination quickly, you may have to opt for expedited shipping services, such as air freight or express shipping. These services are typically more expensive than standard shipping options. As a result, your freight rates will be higher when you require faster delivery due to a shorter lead time.
Capacity and Booking Constraints
Longer lead times often allow shippers more flexibility in booking cargo space on ships, trains, or trucks. When you book well in advance, you may have access to lower rates because carriers can plan their capacity more efficiently. Conversely, when lead times are short, carriers may charge higher rates due to limited availability or increased demand for last-minute shipments.
Inventory Costs
Seasonal Demand
Risk and Insurance
Mode of Transportation
Short lead time has many benefits for both suppliers and customers, such as:
Reducing inventory costs: Short lead time means less inventory in transit and in storage. This reduces inventory holding costs, such as warehousing, insurance, depreciation, obsolescence, etc. It also frees up cash flow and working capital that can be used for other purposes.
Use domestic suppliers
Using a supplier based in the same country as your business can automatically reduce lead time by two weeks or more.
Consider kitting services
Grouping various components that are frequently used together into batches can help workers stay more organized and easily pick what they need from inventory for projects. This process is called “kitting” and increases efficiencies because workers don’t have to spend time counting individual parts.
Grouping various components that are frequently used together into batches can help workers stay more organized and easily pick what they need from inventory for projects. This process is called “kitting” and increases efficiencies because workers don’t have to spend time counting individual parts.
Improve communication and collaboration
Improving communication and collaboration between suppliers, manufacturers, third-party logistics (3PL) or fulfillment providers, shipping companies, and other outside vendors can help reduce lead time.
Use inventory management programs
Inventory management programs can order shipments of items automatically when the inventory level reaches a certain point, reducing the time it takes to process an order and receive the shipment of your products.
Simplify your inventory management and order fulfillment worries with DIDADI Logistics Tech. Streamlining lead times involves managing numerous components, which can be a daunting task when identifying extended lead times within the supply chain.
To enhance your dedication to customer satisfaction, product development, and overall business expansion, DIDADI Logistics collaborates with you to grant access to a global omnichannel fulfillment network across from your China’s suppliers to the US, Canada, Europe, the UK, and Australia.
By teaming up with DIDADI Logistics, you can effortlessly diminish lead times by entrusting inventory management, fulfillment, and shipping processes to seasoned experts .
Recommended Reading